Global stock markets have recovered, as they did in the 1929 slump before they fell and fell:
The current recovery in stocks is due to central banks pumping money into banks which are funnelling it into the finance industry and hence portfolio investments. (QE should be tailored to also reach small and medium sized companies). The central banks cannot do this forever and if a "V shaped" recovery does not happen there will be another strong bear market as in 1930.
The prestigious CPB World Trade Monitor for May has just been published. The News is as expected. The global economy fell off a cliff in May:
There is little point in visiting the CPB figures for May in detail because much has changed since then, in particular the emerging economies have taken a huge hit.
There was no sign of trade recovery in May.
The recovery after the financial crisis in 2010 was not enough to restore the world to the prosperity it had experienced in 2007. The rebound after COVID19 will need to reach 25 to 30% growth to restore our wealth. This seems unlikely.
The UK figures were poor:
The bright spot in the global economy was the Baltic Dry Index (marine cargoes):
Much of the recovery in June was due to an increase in Capesize shipping which are largely coal, ore and commodity etc. shipments (excluding oil - ie: giant bulk carriers that cannot go through the Panama canal). This could be due to shippers feeling more confident that ships will not be stranded in quarantine and manufacturers gambling on a V shaped recovery. The fall in the index in July suggests that any Baltic Dry recovery is fragile.
Lets end this survey on a cheerful note. Lets cheer IHS Markit's Flash PMI surveys show global economy on road to recovery from pandemic to the 24th July, which has this inspiring graphic based on purchase manager sentiment:
Lets hope the PMI is correct!
In the 1930s those countries that ensured that their domestic economies were healthy did best. The global crisis of 1929 was caused by excessive international interdependence of banking, trade and manufacturing. The reduction of this interdependence led to strong growth until it recurred in the 1970s.
After the slump, in the period from 1933-39, when the world was further closing its doors to international trade, international trade plummeted but GDP growth was actually stronger than before.
27/7/2020
The current recovery in stocks is due to central banks pumping money into banks which are funnelling it into the finance industry and hence portfolio investments. (QE should be tailored to also reach small and medium sized companies). The central banks cannot do this forever and if a "V shaped" recovery does not happen there will be another strong bear market as in 1930.
The prestigious CPB World Trade Monitor for May has just been published. The News is as expected. The global economy fell off a cliff in May:
There is little point in visiting the CPB figures for May in detail because much has changed since then, in particular the emerging economies have taken a huge hit.
There was no sign of trade recovery in May.
The recovery after the financial crisis in 2010 was not enough to restore the world to the prosperity it had experienced in 2007. The rebound after COVID19 will need to reach 25 to 30% growth to restore our wealth. This seems unlikely.
The UK figures were poor:
The bright spot in the global economy was the Baltic Dry Index (marine cargoes):
Much of the recovery in June was due to an increase in Capesize shipping which are largely coal, ore and commodity etc. shipments (excluding oil - ie: giant bulk carriers that cannot go through the Panama canal). This could be due to shippers feeling more confident that ships will not be stranded in quarantine and manufacturers gambling on a V shaped recovery. The fall in the index in July suggests that any Baltic Dry recovery is fragile.
Lets end this survey on a cheerful note. Lets cheer IHS Markit's Flash PMI surveys show global economy on road to recovery from pandemic to the 24th July, which has this inspiring graphic based on purchase manager sentiment:
Lets hope the PMI is correct!
In the 1930s those countries that ensured that their domestic economies were healthy did best. The global crisis of 1929 was caused by excessive international interdependence of banking, trade and manufacturing. The reduction of this interdependence led to strong growth until it recurred in the 1970s.
After the slump, in the period from 1933-39, when the world was further closing its doors to international trade, international trade plummeted but GDP growth was actually stronger than before.
Please look at these graphs carefully. Strong growth accompanies drastically reduced international trade. The optimal level of global trading (imports plus exports) for the UK is about 40 to 45% of GDP. Yes, there is an optimal level of global trade for any country - this should surprise no-one.
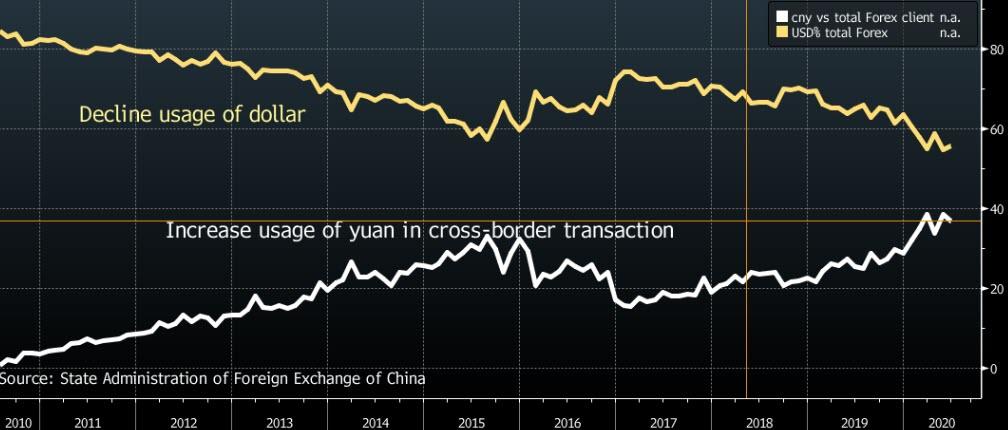
As a final observation, people have been saying for years that the dollar will cease to be the global/reserve currency "soon".
Is "soon" soon? Is there any alternative to the dollar?
Perhaps the decreased use of the dollar by China is a warning:

But China will need to spend its dollars before it can switch to the Yuan.
27/7/2020








Comments